The discovery of ancient artifacts often provides incredible insights into our shared history. However, few finds hold the potential to reshape the historical understanding of a major world religion. Recently, archaeologists unearthed a skeleton adorned with a Christian amulet, sparking discussions that could transform our knowledge of early Christianity’s history. This finding invites us to delve deeper into the origins of Christian practices, symbols, and the potential variations of faith among early Christians.
The Discovery: A Glimpse into the Past
In a groundbreaking excavation, archaeologists uncovered the remains of an ancient skeleton in a burial site that dates back to the early centuries of Christianity. What makes this discovery truly unique is the Christian amulet worn around the neck of the skeleton.

The Christian amulet, intricately designed and inscribed with symbols of Christian faith, appears to date back to the 4th or 5th century. This period was a transformative time for Christianity, marked by the religion’s gradual shift from being persecuted to becoming a dominant spiritual force under the Roman Empire. The artifact’s presence in the burial offers new clues about the ways early Christians expressed their beliefs and practiced their faith.
Why This Amulet Is Significant
- Symbolic Meaning: Early Christian amulet artifacts like amulets were often used as protective talismans, blending religious devotion with mystical beliefs. The discovery suggests that such practices were more widespread than previously thought.
- Historical Context: The design and inscriptions on the amulet could reveal more about the theological debates and regional variations in Christian worship during the time.
- Socio-Cultural Insights: The burial practices associated with the skeleton may provide clues about how Christianity intersected with local traditions.
What Is a Christian Amulet?
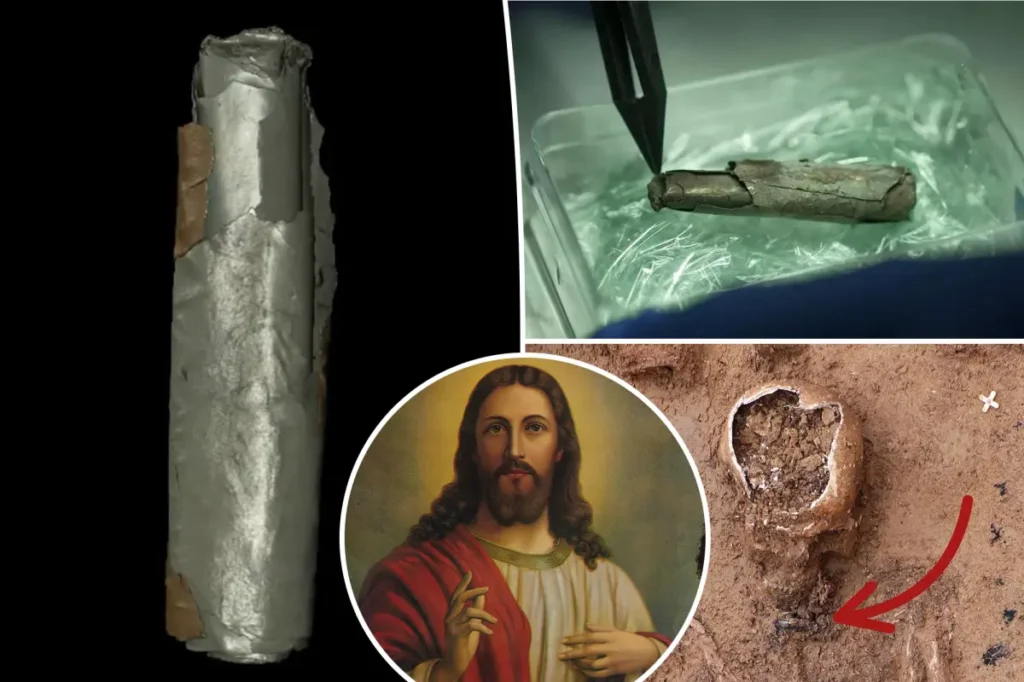
Christian amulet are small, often portable objects inscribed with prayers, crosses, or biblical references. These amulets were believed to offer protection against evil spirits, illnesses, or misfortune, serving as both spiritual and physical safeguards. While some consider them purely devotional items, others interpret them as early examples of syncretism when Christian beliefs merged with older pagan practices.
The Christian amulet found with the skeleton bears the mark of a cross along with ancient inscriptions, which might represent early Christian prayers or verses. This combination hints at how early followers adapted their faith to cultural norms, creating tangible expressions of their spirituality.
How This Amulet Challenges Historical Narratives
The discovery of the skeleton and its Christian amulet could potentially rewrite certain aspects of early Christianity’s history. Here’s why:

1. Unveiling Regional Variations
Early Christian amulet wasn’t a monolithic movement. Different regions practiced faith in diverse ways, influenced by local cultures and traditions. The amulet may provide evidence of regional adaptations of Christianity, revealing how faith was practiced in a specific area.
For instance, the Christianity amulet inscriptions and symbols could differ from those found in other parts of the world, indicating the evolution of Christianity’s expression as it spread. This might challenge the long-held assumption that early Christian worship was uniform.
2. Shedding Light on Underground Christianity
During its early years, Christian amulet often operated clandestinely due to persecution. Artifacts like this amulet suggest that even during times of secrecy, followers found ways to manifest their faith outwardly. This discovery aligns with other findings, such as early Christian graffiti and catacomb paintings, showing how believers practiced their faith in discreet yet meaningful ways.
3. Influence of Pre-Christian Practices
The design and use of the amulet suggest possible remnants of pre-Christian traditions, such as using charms for protection. This Syncretism illustrates how early Christians might have integrated familiar cultural elements into their new faith, making Christianity more accessible to converts.
Amulets and Their Role in Early Christian Life
Artifacts like the one found with the skeleton weren’t merely decorative. They served significant roles in the daily lives of early Christians:
- Protection: Amulets were believed to guard against evil forces, illnesses, and bad luck, echoing pre-Christian protective charms.
- Identity: Wearing a Christian amulet identified the individual as a believer, even in a time when openly declaring one’s faith could be risky.
- Spiritual Connection: These items acted as physical reminders of God’s presence and protection, providing comfort to believers.
The newly discovered amulet, with its unique inscriptions, may also reflect specific prayers or scripture that held deep personal meaning for the wearer.
How Could This Find Rewrite Early Christianity’s History?
This discovery has profound implications for how historians and theologians understand Christianity’s formative years.
1. Expanding the Timeline of Symbol Usage
The detailed craftsmanship of the amulet suggests that Christian symbolism was well-developed earlier than previously believed. It may push back the timeline for the widespread adoption of Christian iconography, such as the cross.
2. Illuminating Burial Practices
Christian burial customs evolved significantly from pagan traditions. The presence of a Christian amulet in a burial context highlights how early Christians honored their dead while maintaining their faith. This could influence future interpretations of burial sites from the same era.
3. Reevaluating the Spread of Christianity
Finds like this demonstrate that Christianity reached regions and social classes beyond what historical texts suggest. Archaeological evidence like the amulet offers tangible proof of the religion’s expansion and adaptability.
Broader Implications for Christianity and Archaeology
1. Bridging the Gap Between Faith and History
Discoveries like the skeleton with the amulet help bridge the gap between the historical Jesus, early Christian communities, and the faith practiced today. They provide a clearer picture of how ancient believers lived out their faith in tangible ways.
2. Encouraging Interdisciplinary Research
This finding emphasizes the importance of combining archaeological techniques with theological and historical studies. By doing so, scholars can unravel the nuanced history of Christianity’s development.
3. Inspiring Modern Believers
For modern Christians, the discovery of such artifacts serves as a powerful reminder of the resilience and creativity of early believers. Understanding their struggles and ingenuity can inspire a deeper appreciation of faith’s journey through history.
Similar Discoveries That Have Shaped Christianity
This isn’t the first time archaeological discoveries have provided new insights into Christianity:

This isn’t the first time archaeological discoveries have provided new insights into Christianity. Over the years, numerous significant finds have contributed to reshaping our understanding of the early Christian world. These discoveries offer glimpses into the lives, beliefs, and practices of Christians in ancient times, sometimes challenging established narratives and providing new perspectives on the evolution of the faith. Here are a few noteworthy discoveries that have had a profound impact on how we understand Christianity’s beginnings:
1. The Dead Sea Scrolls
Discovered between 1946 and 1956 in caves near the Dead Sea, these ancient manuscripts are some of the most important archaeological finds of the 20th century. The scrolls contain fragments of biblical texts, including some of the earliest known copies of books from the Hebrew Bible.
What’s particularly fascinating is the presence of non-biblical writings, including texts that reflect the beliefs and practices of a Jewish sect known as the Essenes, who are believed to have lived during the time of Jesus. The scrolls shed light on the religious environment in which Christianity emerged and offered new insights into the diversity of Jewish thought and practice at the time. They also helped historians understand the development of Christian theology, particularly in relation to messianic expectations.
2. The James Ossuary
The discovery of a limestone burial box, or ossuary, in 2002 made headlines around the world. Inscribed with the words “James, son of Joseph, brother of Jesus,” the ossuary is believed to have belonged to James, the brother of Jesus and a prominent figure in early Christianity.
While its authenticity has been debated, the ossuary offers intriguing evidence of the historical existence of Jesus and his family. This find is significant because it provides a direct link to Jesus’ earthly family and supports the historical context in which early Christianity began. It also highlights the role of Jesus’ relatives in the formation of the early Church.
3. The Chi-Rho Symbol
The Chi-Rho is an early Christian symbol composed of the first two letters of the Greek word for Christ (Χριστός). Found in numerous early Christian sites, including catacombs and churches, the Chi-Rho became a prominent symbol of Christianity in the Roman Empire.
One of the most famous examples of its use is on the shield of the Roman Emperor Constantine, who adopted it as part of his battle standard before the pivotal Battle of the Milvian Bridge in 312 CE. The victory, attributed to the Christian god, marked the beginning of Christianity’s rise to prominence within the Roman Empire. The Chi-Rho symbol is significant because it demonstrates how early Christians used symbols to express their faith in an environment that often viewed them with suspicion and hostility.
4. Christian Graffiti in the Catacombs
The catacombs of Rome, sprawling underground burial sites used by early Christians, are a rich source of archaeological evidence. Among the many discoveries in the catacombs are examples of Christian graffiti simple carvings made by early Christians on the walls of their underground tombs.
These inscriptions include Christian symbols, like the fish and the Chi-Rho, and sometimes even short prayers or phrases like “Jesus Christ, Son of God.” These early inscriptions are significant because they demonstrate the clandestine nature of Christian worship during periods of persecution. The catacombs also offer valuable insights into early Christian burial practices and the ways in which faith was lived out in secret.
5. The Gospel of Judas
In 1978, a manuscript known as the Gospel of Judas was discovered in a cave in Egypt. The gospel is a Gnostic text that presents a radically different account of Judas Iscariot’s role in Christian tradition. Contrary to the traditional view of Judas as the betrayer of Jesus, the Gospel of Judas portrays him as acting in accordance with Jesus’ wishes, fulfilling a divine plan.
Although the text was not included in the New Testament canon, its discovery opened new discussions on the diversity of early Christian beliefs and the existence of alternative gospels that were not widely accepted by orthodox Christianity. The Gospel of Judas has sparked debates among scholars and theologians regarding the early formation of Christian doctrine and the interpretation of key biblical events.
The skeleton with the Christian amulet joins these ranks as a discovery with the potential to redefine our understanding of early Christian life and beliefs.
Key Takeaways
- A Rare Artifact: The Christian amulet found with the skeleton provides unique insights into early Christian practices.
- Challenging Assumptions: The discovery calls into question long-held beliefs about the uniformity of early Christianity.
- Broader Context: The find highlights the intersection of faith, culture, and history in shaping religious practices.
The discovery of a skeleton wearing a Christian amulet has the potential to rewrite early Christianity’s history, offering fresh insights into the faith’s regional variations, cultural adaptability, and personal expressions. Such findings remind us that history is not static but constantly evolving as new evidence emerges.
For believers, historians, and archaeologists alike, this discovery provides an opportunity to delve deeper into the rich tapestry of Christianity’s early years. As we uncover more about the lives of early Christians, we gain not only historical knowledge but also a greater appreciation of the resilience and creativity that shaped one of the world’s most influential religions.