Smart Glasses: The Rise of Meta
In the rapidly evolving world of wearable technology, Meta’s Smart Glasses have emerged as one of the most ambitious ventures aimed at redefining how we interact with the digital and physical worlds. With sleek designs, augmented reality (AR) capabilities, and seamless integration with social platforms, Meta’s Smart Glasses promised to be a revolutionary product. Marketed as both a fashion-forward and function-heavy innovation, these smart glasses symbolized the company’s bold pivot from social networking to a broader metaverse vision.
Yet, as Meta’s Smart Glasses have started to gain traction, a wave of legal challenges has begun to surface, raising concerns over privacy, data protection, intellectual property, and regulatory compliance. What was once an exciting frontier is now a legal battleground, forcing stakeholders to ask a critical question: Is Meta pushing too far, too fast?
The Vision Behind Meta’s Smart Glasses
When Meta (formerly Facebook) unveiled its plans for Meta’s Smart Glasses, the company made its intentions clear it was no longer just a social media giant but a pioneer of the metaverse. The smart glasses were developed in collaboration with EssilorLuxottica, the parent company of Ray-Ban, aiming to combine cutting-edge AR capabilities with everyday eyewear aesthetics.
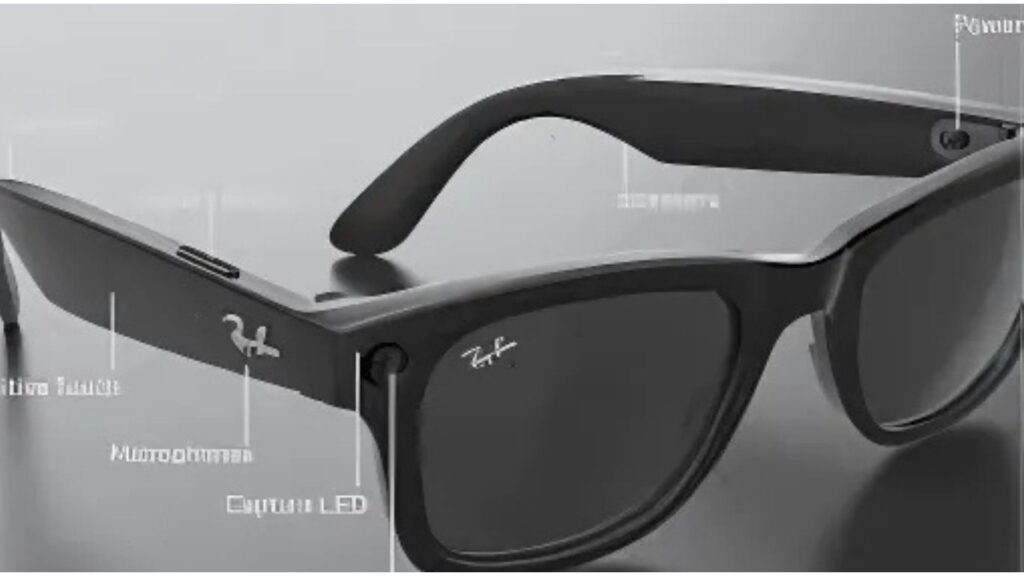
The first generation of Meta’s Smart Glasses featured audio input/output capabilities, built-in cameras for photo and video capture, and touch-sensitive controls. The future roadmap teased more immersive AR overlays, live-streaming integration, spatial audio, and voice assistant functions. All of these features were meant to act as a bridge between the real and digital environments, gradually bringing users into Meta’s evolving metaverse ecosystem.

Privacy Concerns Spark Backlash
As exciting as the technology sounds, the very capabilities that make Meta’s Smart Glasses impressive also raise major privacy red flags. The ability to discreetly record video and audio using built-in cameras has alarmed consumer advocacy groups, government agencies, and privacy watchdogs.
One of the most serious concerns is the lack of informed consent. Unlike a smartphone, which is overtly visible during use, Meta’s Smart Glasses allow users to record others without them realizing it. This silent surveillance feature has triggered debates around the right to privacy in public and private settings.
Several countries, including Germany and Canada, have initiated investigations into whether Meta’s Smart Glasses violate national data protection laws. Critics argue that Meta has failed to implement sufficient indicators (like visible lights or sound notifications) to alert people when recording is in progress.
Regulatory Scrutiny Intensifies
Beyond public concerns, regulatory bodies have started to scrutinize Meta’s Smart Glasses under the lens of national and international laws. In the European Union, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has been a major point of contention. Under GDPR, companies are required to ensure transparency in data collection and obtain explicit consent before recording or storing personal data.
Authorities in Ireland, where Meta’s European headquarters are located, have opened inquiries into how Meta handles the vast amounts of audio-visual data collected via its smart glasses. Questions remain over whether Meta has a lawful basis for processing such data and if the data subjects have been adequately informed.
In the United States, lawmakers have called on the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) to evaluate whether Meta’s Smart Glasses comply with consumer protection standards. The FTC is reportedly reviewing complaints about deceptive practices and the lack of safety guidelines for the public.
Intellectual Property Disputes
Another legal challenge facing Meta’s Smart Glasses comes from the realm of intellectual property. Several smaller tech companies and patent holders have filed lawsuits claiming that Meta has infringed on their AR-related technologies. These lawsuits accuse Meta of copying key components related to gesture control, spatial tracking, and lens technology without licensing agreements.
One notable case involves a Silicon Valley startup that alleges Meta unlawfully integrated its patented AR processing framework into the hardware of Meta’s Smart Glasses. Although Meta has denied any wrongdoing, the case has moved into federal court, raising the stakes for both parties.
If Meta is found liable, it could face hundreds of millions in fines and may need to redesign core aspects of its smart glasses a development that could severely disrupt its product pipeline and damage its metaverse vision.
Workplace Surveillance Controversies
Another area where Meta’s Smart Glasses have sparked concern is workplace surveillance. Companies intrigued by wearable AR are exploring these smart glasses for employee monitoring and task optimization. While potentially useful for logistics and manufacturing sectors, this use case opens a Pandora’s box of ethical dilemmas.
Labor unions and employee rights groups argue that Meta’s Smart Glasses could enable intrusive surveillance in the workplace. By allowing managers to watch live feeds or review recordings of workers, employers might violate labor laws or collective bargaining agreements that protect employee privacy.
Legal experts warn that without clear regulations, using Meta’s Smart Glasses in corporate settings could lead to a flood of employment-related lawsuits. Already, several complaints have been filed in California and New York by employees who claim they were unknowingly monitored through wearable devices.
Data Security Risks
With Meta’s Smart Glasses collecting and transmitting vast amounts of real-time data, cybersecurity is another legal minefield. Any breach of this data, whether through hacking, unauthorized access, or internal misuse could expose sensitive personal information.
Cybersecurity researchers have identified potential vulnerabilities in the glasses’ firmware and cloud syncing mechanisms. These flaws could allow hackers to access live video feeds, location data, and even audio recordings.
In a worst-case scenario, such vulnerabilities could be exploited for stalking, blackmail, or corporate espionage. Legal frameworks like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and GDPR have provisions for such scenarios, and if Meta fails to demonstrate adequate cybersecurity measures, it could face steep penalties and mandatory audits.
Public Backlash and Brand Reputation
The accumulation of legal woes surrounding Meta’s Smart Glasses has also started to affect the company’s public image. While Meta is no stranger to controversy having faced multiple scandals over user data misuse and platform manipulation the backlash over smart glasses is particularly damaging due to the physical and intimate nature of the device.
Unlike social media platforms that users can choose to log out of, Meta’s Smart Glasses are worn and integrated into everyday life. The idea that someone next to you could be silently recording your movements or conversations has provoked strong emotional reactions from the public.
In response, Meta has attempted to launch PR campaigns emphasizing transparency and consent features. However, critics argue that these measures are reactive rather than proactive, and the company’s history of privacy violations makes it difficult to trust such reassurances.
Legal Risk to the Broader AR Industry
The legal challenges facing Meta’s Smart Glasses could also have ripple effects throughout the broader augmented reality industry. If courts establish strict legal precedents for privacy, data handling, and IP compliance, other companies developing similar wearable technologies will need to follow suit.
For startups and smaller firms, these legal barriers could become insurmountable, stifling innovation in a sector that relies on rapid iteration and experimentation. Conversely, well-capitalized companies like Apple and Microsoft may benefit, as they already possess legal teams and compliance infrastructure to navigate these complex regulations.
Industry analysts warn that if Meta fails to overcome its legal battles, it could delay mainstream adoption of AR wearables by several years.
Meta’s Legal Strategy: Defend, Settle, or Adapt?
Faced with multiple legal fronts, Meta must now make strategic decisions about how to manage the risk. The company has reportedly begun hiring more legal experts specializing in international privacy law, IP litigation, and cybersecurity compliance.
Some lawsuits are expected to result in settlements, while others may go to trial. In parallel, Meta is believed to be working on updated versions of its smart glasses that include stronger privacy indicators, better data encryption, and opt-in recording notifications.
Still, legal experts caution that compliance retrofits may not be enough to rebuild public trust or satisfy regulators. To truly overcome this legal storm, Meta may need to redesign not just its smart glasses but its entire approach to user data in the physical world.
What’s Next for Meta’s Smart Glasses?
Despite the legal setbacks, Meta shows no signs of halting its wearable tech ambitions. Meta’s Smart Glasses remain central to the company’s long-term strategy of building the metaverse, and the next generation is rumored to include advanced AR overlays, real-time language translation, and health-monitoring features.
However, the success of these future models will heavily depend on how Meta addresses the current legal landscape. Enhanced transparency, consent-based interactions, and robust security features must be built into the core design not added as an afterthought.
Meta also faces pressure from investors who are closely watching the cost of ongoing lawsuits and regulatory fines. If Meta’s Smart Glasses continue to invite legal scrutiny without meaningful reform, shareholder confidence could erode, leading to internal restructuring or product delays.
Lessons for the Tech Industry
The controversy surrounding Meta’s Smart Glasses serves as a critical case study for tech firms innovating in the realm of wearable devices. The lesson is clear: bold innovation must be paired with ethical responsibility and legal foresight.
Companies must consider not just what technology can do, but what it should do. This involves collaborating with regulators, privacy experts, and civil society to develop frameworks that protect individual rights while fostering innovation.
For Meta, the road ahead is uncertain. Meta’s Smart Glasses represent both a pioneering vision and a cautionary tale. How the company navigates this legal storm will likely influence not only its future but the entire trajectory of consumer-focused AR technology.