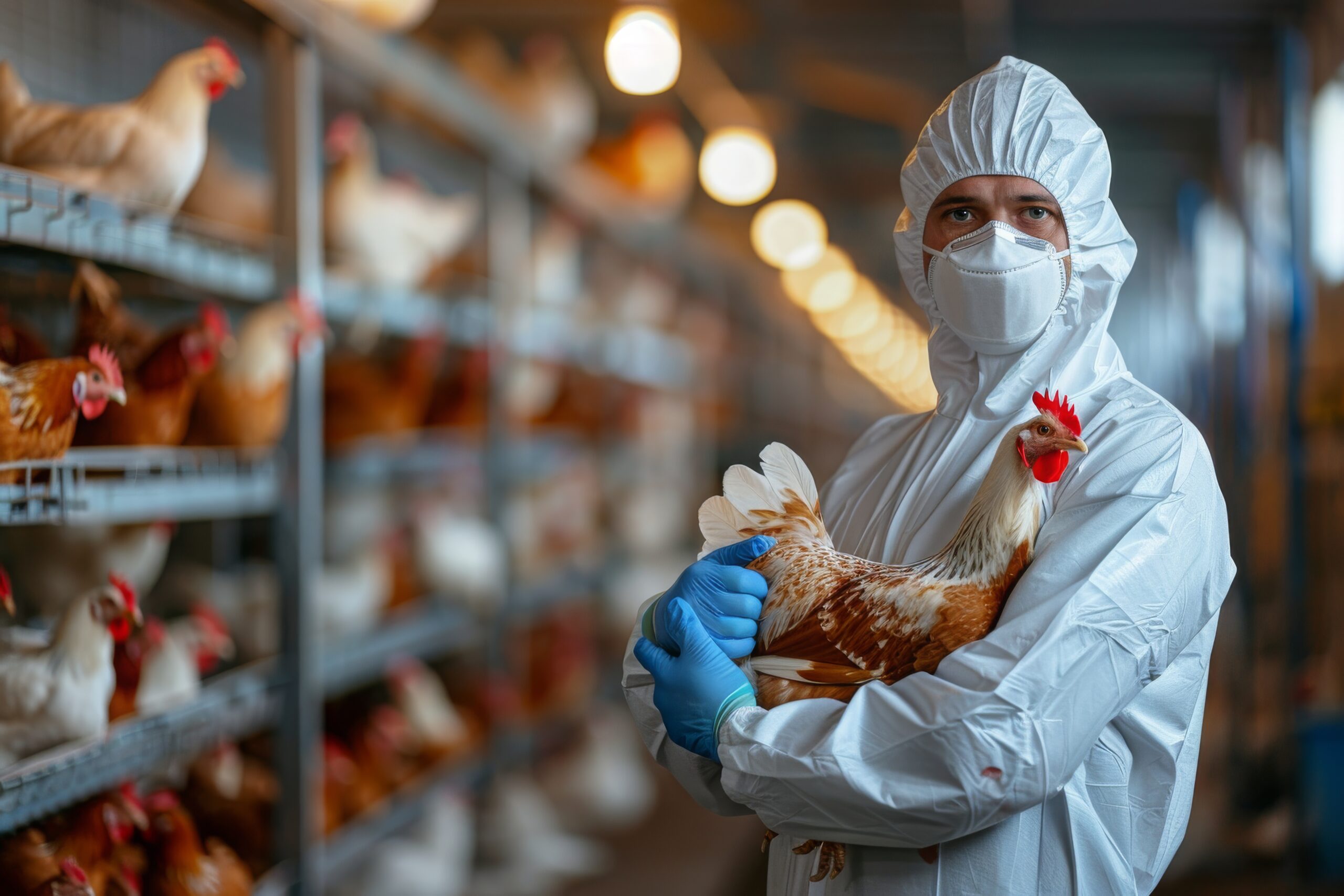
The world is no stranger to health crises, with global leaders always on alert for the next potential pandemic. Recently, the bird flu virus has emerged as a growing concern, with experts warning that the situation could escalate. The bird flu pandemic is a looming threat, with increased cases of avian influenza spreading across various regions, affecting both animal and human populations.
The Surge of Bird Flu Cases Around the World
In recent months, a surge in bird flu cases has raised alarm worldwide. Governments and health authorities are closely monitoring the situation, with fears that the virus could mutate and trigger a global pandemic. While bird flu has been around for years, its recent spread and the mutation of certain strains have made experts more concerned than ever before. As of 2025, the H5N1 strain is being heavily scrutinized, not only because of its ability to infect birds but also due to its potential to infect humans.

What is Bird Flu and Why is it Dangerous?
Bird flu, also known as avian influenza, is a viral infection that primarily affects birds but can also spread to humans and other animals. The virus is highly contagious among birds, and in severe cases, it can lead to death. Although human cases are rare, the virus has been known to mutate, making it capable of spreading between humans in some circumstances.
The bird flu virus typically spreads through bird-to-bird contact and via contaminated environments, making poultry farms particularly vulnerable. If humans become infected, the symptoms resemble those of the flu and can range from mild to severe, depending on the strain of the virus. In some cases, the infection can be fatal. The H5N1 strain, for example, has shown a concerning mortality rate in humans.
What makes bird flu even more dangerous is its ability to mutate into forms that can be transmitted from human to human. While there has been no widespread human-to-human transmission yet, experts fear that the virus could evolve in the future, making it more contagious. A mutation of this nature could potentially lead to the outbreak of a bird flu pandemic, which is why global health experts are urging leaders to prepare for such a scenario.
The Spread of Bird Flu Among Animals
The recent surge in bird flu cases has been alarming, particularly in poultry farms and wild bird populations. The virus is believed to have spread through migrating birds, making it difficult to contain. As of recent reports, certain regions, such as Idaho in the United States, have seen significant outbreaks among dairy cattle, further complicating efforts to control the virus. This transmission from birds to other animals, such as cattle, is a concerning development, as it suggests that the virus can spread across species, amplifying the potential for mutation.
The highly pathogenic H5N1 strain of the bird flu has been responsible for many of these outbreaks. This strain has been identified as particularly dangerous due to its potential to mutate into a form that could be easily transmitted to humans. While experts continue to monitor the situation, the rapid spread of bird flu among animals poses a significant challenge to public health. The spread through wild birds further complicates efforts to control it, as migratory patterns make it harder to trace and contain the outbreaks.
The Human Impact of Bird Flu: Potential for a Pandemic
Although human-to-human transmission of bird flu remains rare, the possibility of such transmission is enough to make health experts wary. The H5N1 strain, in particular, has shown a capacity for mutation, which could lead to a situation where the virus spreads easily between humans. This potential for mutation is what makes the bird flu pandemic such a pressing concern.
In addition to the risk of mutation, the spread of bird flu can have devastating effects on global food supplies. Poultry farmers are already feeling the impact, with mass culling of infected birds being the primary method of controlling the outbreak. The disruption of the food supply chain could have far-reaching consequences, including skyrocketing prices and shortages of essential food items. Countries that rely heavily on poultry for both domestic consumption and export are especially vulnerable. The pandemic not only threatens public health but also the global economy.
The disease has also had a severe impact on animal agriculture, with millions of birds being culled to prevent the spread. While this is necessary to protect the population from the virus, the economic toll on farmers, especially in regions where poultry farming is a significant part of the economy, is devastating. This challenge is compounded by the fact that the virus can survive in the environment for long periods, complicating efforts to disinfect farms and prevent further outbreaks.
Governments and Experts Urge Preparedness
As the threat of a bird flu pandemic grows, governments worldwide are being urged to ramp up their preparedness efforts. Leaders are being advised to take proactive measures to prevent the spread of the virus and to develop contingency plans in case the situation worsens.
Surveillance and Monitoring
One of the key measures being implemented is increased surveillance of both wild birds and domesticated poultry. By closely monitoring the health of bird populations, health authorities can identify outbreaks early and take swift action to prevent the virus from spreading further. Surveillance also extends to human populations, with health authorities keeping a close eye on any potential cases of bird flu in humans. Early detection is critical in preventing a potential pandemic, as the virus can spread rapidly once it mutates into a more easily transmissible form.
The surveillance network being set up is extensive, involving not just local health authorities but international bodies as well. Agencies like the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) are actively collaborating to monitor outbreaks and share critical information. This global effort is essential to prevent the spread of the virus across borders and to contain any potential outbreaks as quickly as possible.
Vaccine Development and Stockpiling
Vaccine development has also become a critical part of the preparedness strategy. Researchers are working tirelessly to create effective vaccines that could protect against bird flu strains, especially H5N1. While it’s still early in the process, the goal is to develop vaccines that could be rapidly deployed if a pandemic were to occur. Vaccine stockpiling is a necessary part of this effort, ensuring that doses are available in the event of an outbreak.
In addition to vaccine development, stockpiling essential medical supplies is also a priority. Governments are being advised to stockpile antiviral medications, personal protective equipment, and other medical resources that could be needed in the event of a bird flu outbreak. The stockpiling of vaccines and medical supplies is a precautionary measure to ensure that countries are well-equipped to handle an outbreak and limit its impact.

The Role of the Public in Preventing the Bird Flu Pandemic
While governments and health organizations play a crucial role in preventing the spread of bird flu, the public also has a part to play in minimizing the risk. Individuals are encouraged to practice good hygiene, avoid contact with sick animals, and report any signs of bird flu in poultry or wild birds.
Educating the Public About Bird Flu
Public education campaigns are essential in raising awareness about bird flu and how it spreads. Governments and health organizations are working to inform the public about the symptoms of bird flu in both humans and animals and how to take preventive measures to reduce the risk of exposure. Understanding the transmission dynamics of the virus is essential, as it can help people take appropriate steps to protect themselves and their families.
In addition to educating the public about the symptoms and transmission of bird flu, health authorities are also focusing on how people can limit their exposure to the virus. For example, individuals living in areas with high levels of bird flu should avoid handling sick or dead birds, and poultry farmers are advised to take extra precautions when caring for their flocks. Regular handwashing and the use of personal protective equipment are also essential practices to reduce the risk of infection.
What Can You Do to Protect Yourself?
For the general public, staying informed and taking precautions is key. If you live in an area where bird flu has been detected, it’s important to avoid close contact with poultry and to report any unusual bird deaths to local authorities. In addition, maintaining good hygiene practices, such as washing hands frequently and wearing protective gear when handling animals, can help reduce the risk of infection.
For those who work in poultry farming or in environments where exposure to birds is high, additional precautions may be necessary. This may include wearing gloves, masks, and other protective clothing to prevent contamination. Similarly, those in healthcare and veterinary professions should adhere to strict infection control protocols to minimize the risk of exposure.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of bird flu cases, both in animals and humans, is essential in preventing the virus from spreading further. Health authorities encourage people to seek medical attention if they experience flu-like symptoms, particularly if they have had contact with animals or birds. Early intervention can prevent the virus from becoming more widespread and can save lives.
Local authorities play a crucial role in early detection by closely monitoring at-risk populations. Hospitals and healthcare clinics are equipped to detect potential cases of bird flu through laboratory testing, and they are encouraged to report any unusual cases to health agencies. The quicker a case is identified, the faster preventive measures can be implemented to stop the virus from spreading.
Global Response: Collaborating for a Better Future
The bird flu pandemic is a global issue that requires a collaborative response from governments, health organizations, and the public. By working together, we can develop the tools and strategies needed to prevent the spread of the virus and minimize its impact.
Strengthening International Cooperation
International cooperation is crucial in addressing the bird flu pandemic. The World Health Organization (WHO) and other global health bodies are playing an active role in coordinating efforts to combat the virus. Through sharing information, resources, and expertise, nations can better prepare for potential outbreaks and respond more effectively when they occur. This international collaboration is vital for ensuring that no country is left behind in the fight against the bird flu pandemic.
Global cooperation is also essential in ensuring that vaccines and medical treatments are distributed equitably. Countries with fewer resources may struggle to procure the necessary supplies, and international organizations are working to ensure that developing nations receive support in their efforts to combat the virus.
Research and Innovation
Research into bird flu and other infectious diseases is essential for developing new strategies to combat these viruses. By investing in scientific research, we can develop better vaccines, improve diagnostic tools, and create more effective treatments for those affected by bird flu. Governments, universities, and private organizations are collaborating on this research, which is expected to lead to breakthroughs that could prevent future pandemics.
The focus on research and innovation will be critical in ensuring that the world is prepared for any future pandemics, including those caused by bird flu. As scientists learn more about how the virus spreads and how it mutates, they will be better equipped to create solutions that can stop it in its tracks.
The Future of the Bird Flu Pandemic
As the bird flu continues to spread and evolve, it is clear that the potential for a global pandemic remains a significant concern for health authorities worldwide. The virus’ ability to mutate and its rapid spread across regions only heightens the urgency of this issue. While much progress has been made in monitoring the virus, improving surveillance systems, and developing preventive measures, there is still much work to be done to ensure that we are fully prepared to prevent a widespread outbreak. The situation demands ongoing vigilance and a commitment to staying ahead of the virus as it continues to evolve.
The key to managing the bird flu pandemic will be continued vigilance, effective preparedness strategies, and collaboration across all sectors. Only by working together can we hope to reduce the impact of bird flu and prevent it from becoming the next global health crisis.